others-prepare for cks exam with me 13: Container runtimes(gVisor/Kata containers) in Kubernetes
1. Purpose
In this post, I would continue to write about preparing for the CKS (Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist) exam. I would write my own notes about the exam, and you can refer to these articles to prepare your own.
List of the series of posts:
-prepare for cks exam with me 1: Linux user and group management
-prepare for cks exam with me 2: Linux ssh hardening
-prepare for cks exam with me 3: Linux remove obsolete packages and services
-prepare for cks exam with me 4: Linux kernal hardening
-prepare for cks exam with me 5: Linux UFW(Uncomplicated firewall)
-prepare for cks exam with me 6: Seccomp in Linux, Docker and Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 7: Apparmor in Linux, Docker and Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 8: Security context in Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 9: Admission controllers in Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 10: Pod security policy in Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 11: Open policy agent in Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 12: Secrets in Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 13: Container runtimes(gvisor/kata containers) in Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 14: Container Image security in Docker and Kubernetes
-prepare for cks exam with me 15: How to print docker images of all pods in kubernetes
2. Environment
- CKS
- Ubuntu System
3. Container runtimes in Kubernetes
3.1 What is container runtime?
When we call the following command in host
$ docker run -d nginx
In fact, we are calling docker daemon restful service to create a container process. There are a few steps under the hood, the last step is creating containers by runc.
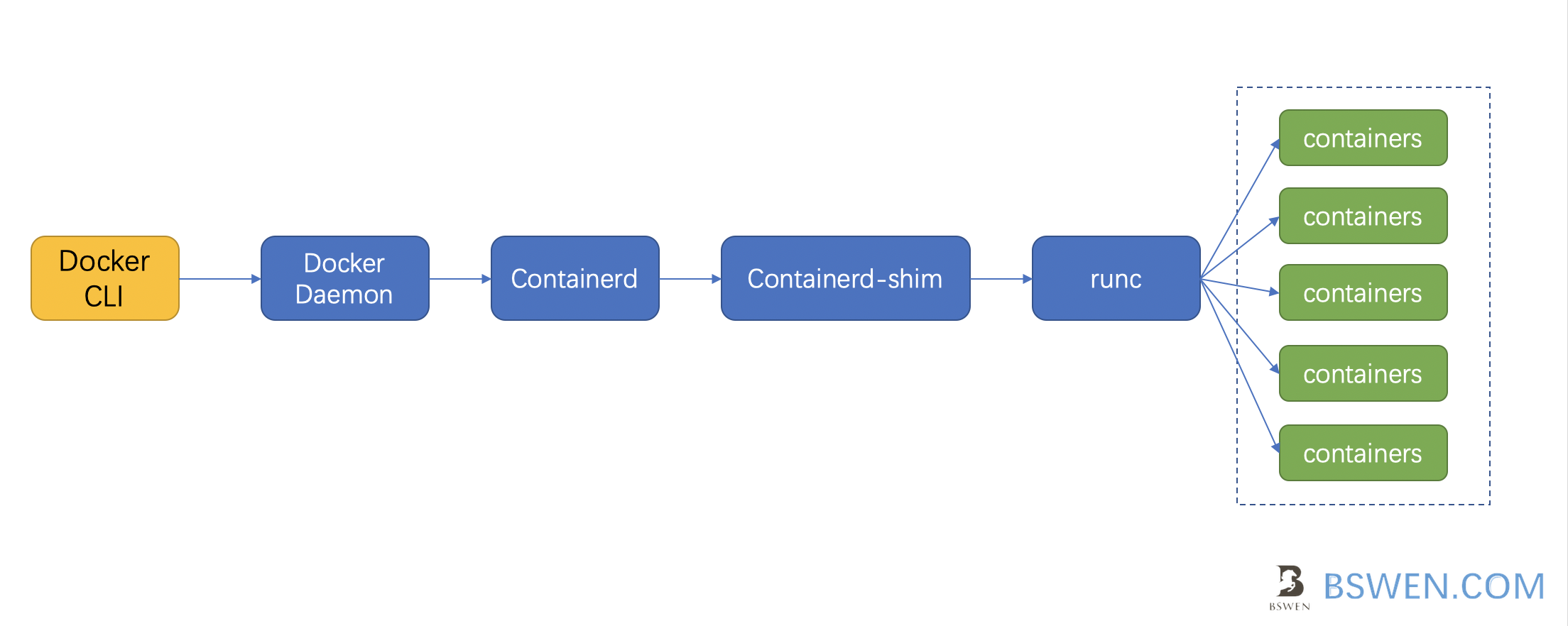
What is runc?
runC is a lightweight, portable container runtime. It includes all of the plumbing code used by Docker to interact with system features related to containers.
There are two standards about container runtimes, one is OCI (by Docker), the other is CRI (by kubernetes).Here is the list of the container runtimes:
- Open Container Initiative (OCI) Runtimes
- Native Runtimes
- runC
- rkt
- Sandboxed and Virtualized Runtimes
- gviso
- runV
- kata-containers
- Native Runtimes
- Container Runtime Interface(CRI)
- containerd
- cri-o
3.2 What is gVisor?
gVisor is a sandboxed container runtime developed by Google, its main purpose is to solve the security problems that caused by the kernel sharing of all containers on the host.
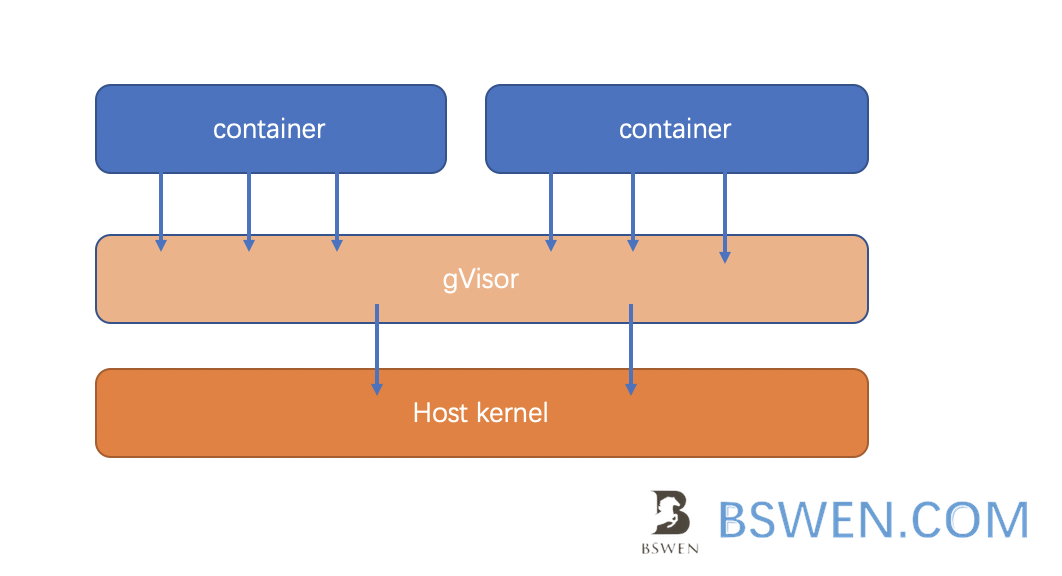
Just as the above picture shows, the gVisor provide the containers with limited syscalls. Only filtered system calls can reach the host kernel, so the attack interface is smaller.
3.3 What is kata container?
The kata container allows each container to have a lightweight system kernel, so that the container calls its own kernel instead of sharing the kernel.
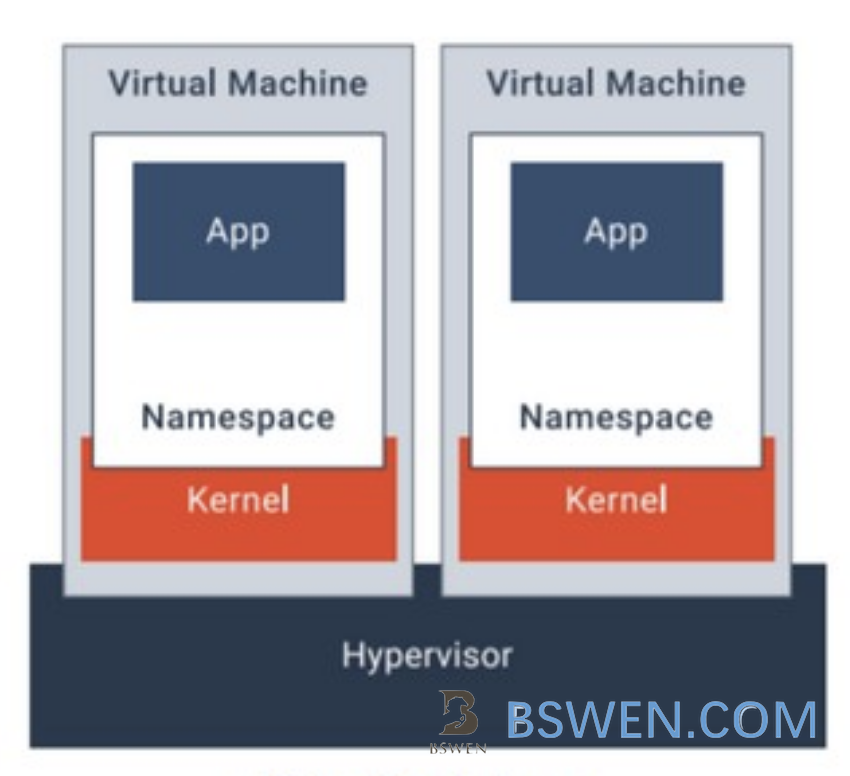
Compared to the gVisor runtime, the kata container provides the containers with a dedicated lightweight kernel , so the system calls are mostly inside the container’s own kernel. The host kernel is safer than gVisor.
3.4 How to switch runtimes by using docker?
We can switch to different container runtimes by running the following command:
# gvisor
$ docker run —-runtime runsc -d nginx
# kata
$ docker run —-runtime kata -d nginx
3.5 How to change container runtimes in Kubernetes?
We can define RuntimeClass in kubernetes:
apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1 # RuntimeClass is defined in the node.k8s.io API group
kind: RuntimeClass
metadata:
name: myclass # The name the RuntimeClass will be referenced by
# RuntimeClass is a non-namespaced resource
handler: myconfiguration # The name of the corresponding CRI configuration
For example, we can define gVisor and kata container runtime classes as follows:
apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1
kind: RuntimeClass
metadata:
name: gvisor
handler: runsc
---
apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1
kind: RuntimeClass
metadata:
name: kata
handler: kata
Then we can list the container runtimes in kubernetes:
$ kubectl get runtimeclass
3.6 How to configure the runtimeClass for pods in kubernetes?
Now we have RuntimeClass in kubernetes, we can configure pods to use them:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
runtimeClassName: myclass
# ...
For example, we want to configure a nginx pod to use gVisor runtime:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
runtimeClassName: gvisor
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
4. Summary
In this post, I write some examples about container runtimes(gvisor/kata containers) in kubernetes.