How to resolve 502 bad gateway error when using proxy_pass in Nginx and Tomcat?
1. Introduction
In this post, I will demonstrate how to resolve the 502 bad gateway error when using proxy_pass in Nginx.
2. Environment
- Nginx 1+
3. The nginx.conf
We can define an upstream to reverse proxy local Tomcat services running on localhost as follows:
The service layout:
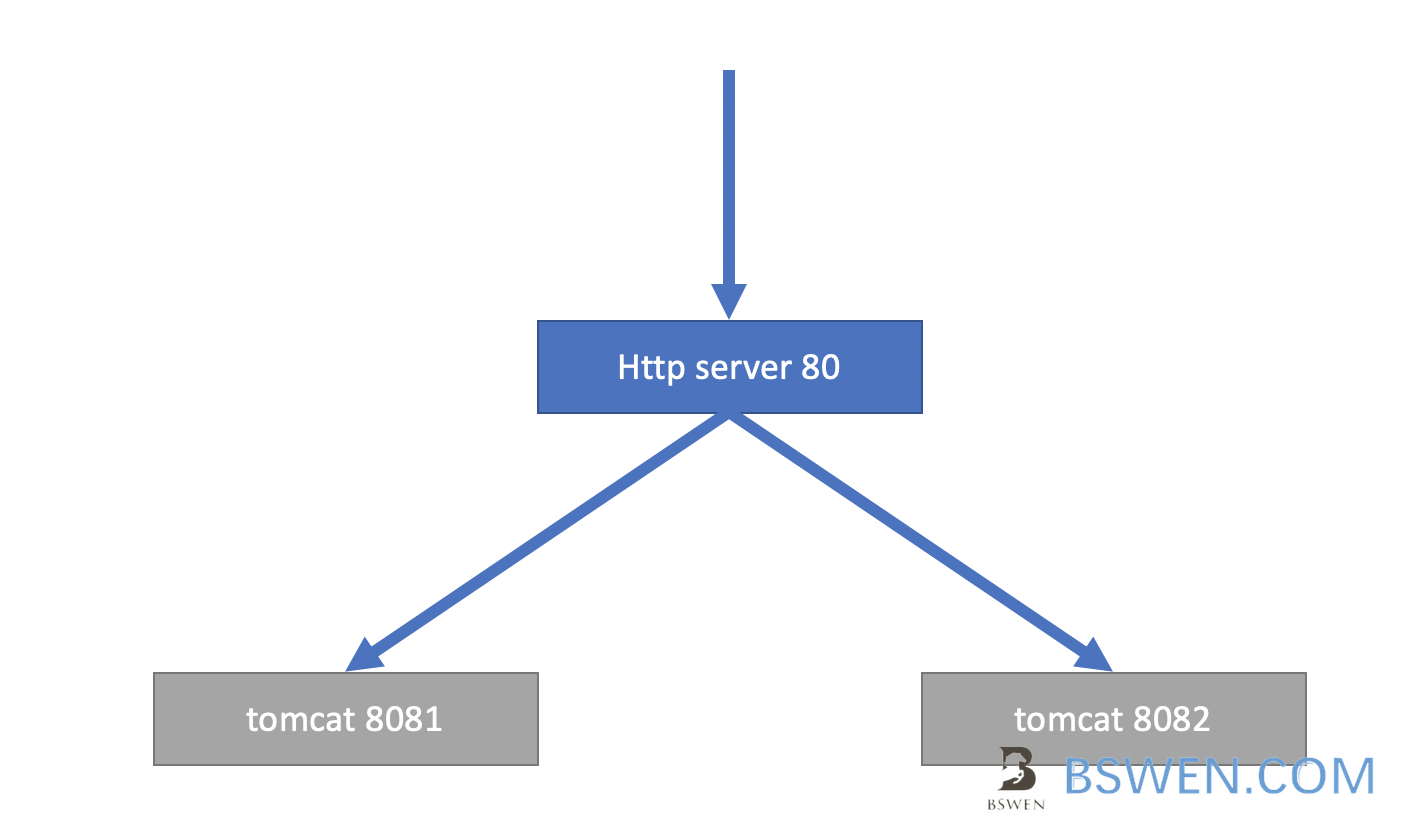
HTTP { ... # define an upstream to be reversely proxied # There are two local tomcat services that are listening to port 8081 and 8082 upstream service { server localhost:8081; # tomcat 1 server localhost:8082; # tomcat 2 } ... #define a server to proxy the services server{ listen 80; ... location /myservice { proxy_pass http://service; } }}When a user navigates to http://xxx.com/myservice, the request will be reverse proxied to the Tomcat instances running on localhost (ports 8081 and 8082).
4. The problem
When your business grows, the number of concurrent HTTP requests may surge in a short period, as a result, your users might encounter an error like this when attempting to access your services:
<html> <head> <title>502 Bad Gateway</title> </head> <body bgcolor="white"> <center> <h1>502 Bad Gateway</h1> </center> <hr> <center>nginx</center> </body></html>5. How to resolve this 502 bad gateway problem?
5.1 Why did this happen?
Default HTTP 1.0 connections and requests:
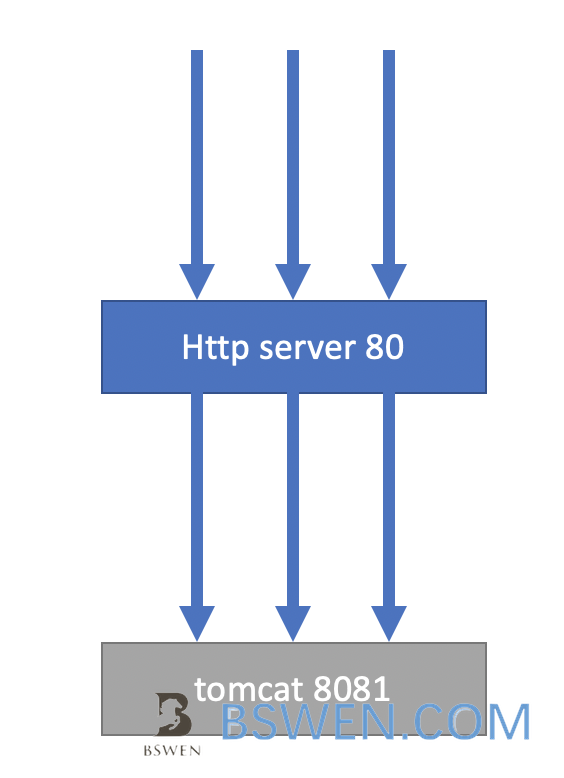
You can see that every request create a new connection,so your server would suffer from the surge requests.
The HTTP 1.1 connections and requests:
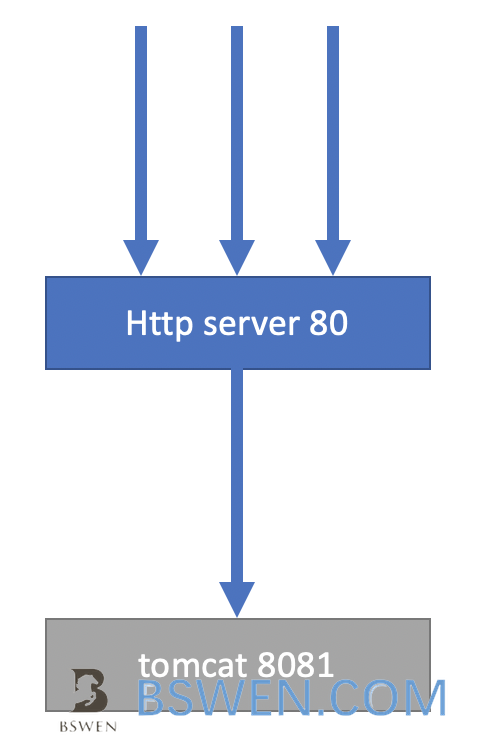
You can see that there are only a few connections between the nginx and local service, many of them are reused between HTTP requests.
5.2 Try to use HTTP Keep-Alive feature
Change your server settings in nginx.conf, try to activate HTTP 1.1 keep-alive features like this:
#define a server to proxy the services server{ listen 80; ... location /myservice { proxy_HTTP_version 1.1; #use HTTP 1.1 to connect local service proxy_set_header Connection ""; #remove client connection headers
proxy_pass http://service; } }The explanation:
proxy_HTTP_version 1.1indicates the use of HTTP 1.1, as the keep-alive feature is a default feature in HTTP 1.1 protocol.proxy_set_header Connection ""is used to clear the client’s connection headers and to utilize the HTTP/1.1 header.
5.3 Set the maximum number of idle Keep-Alive connections for the upstream server
Change your upstream settings like this:
HTTP { ... # define an upstream to be reversely proxied # There are two local tomcat services that are listening to port 8081 and 8082 upstream service { # The keepalive parameter sets the maximum number of idle keepalive connections # to upstream servers that are preserved in the cache of each worker process. When # this number is exceeded, the least recently used connections are closed. keepalive 50;
server localhost:8081; # tomcat 1 server localhost:8082; # tomcat 2 } ...}And,
The keepalive_timeout directive in the NGINX configuration specifies the amount of time that a connection should be kept open after the last request. This helps to reduce the overhead of establishing new connections for subsequent requests. In simple terms, it controls how long NGINX should wait before closing an idle connection.
6. The final nginx.conf
Here is the final nginx.conf file content:
HTTP { #change the default 15 seconds to 5 seconds to decrease the load of the server keepalive_timeout 5; ... # define an upstream to be reversely proxied # There are two local tomcat services that are listening to port 8081 and 8082 upstream service { # The keepalive parameter sets the maximum number of idle keepalive connections # to upstream servers that are preserved in the cache of each worker process. When # this number is exceeded, the least recently used connections are closed. keepalive 50;
server localhost:8081; # tomcat 1 server localhost:8082; # tomcat 2 } ... #define a server to proxy the services server{ listen 80; ... location /myservice { proxy_HTTP_version 1.1; #use HTTP 1.1 to connect local service proxy_set_header Connection ""; #remove client connection headers
proxy_pass HTTP://service; } }}6. Summary
You should always try to use the keep-alive feature of HTTP, it will help you to obtain good user experience and good revenue too.